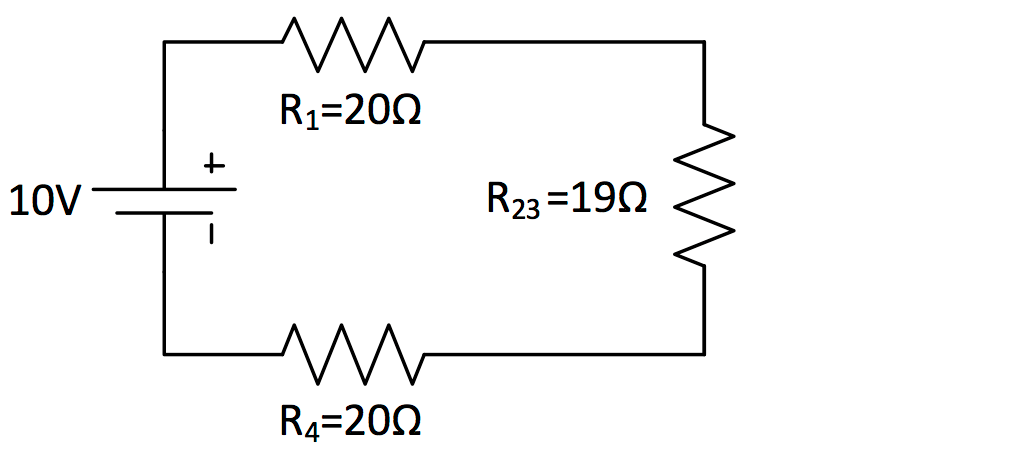
It = i1 = i2 = i3… given 120 v as the total voltage, and . Equivalent resistance and current in a parallel circuit. On a series circuit they should equal the voltage increase of the power supply. In the circuit shown at the right, a voltage of 6 v pushes charge through a single resistor of 2 ω. Select intro and build the simple series circuit included in this lesson.
Equivalent resistance and current in a parallel circuit.
On a series circuit they should equal the voltage increase of the power supply. Series circuits are the simplest to work with. This equation can be used for any number of resistors in parallel. Select intro and build the simple series circuit included in this lesson. A tutorial on how to solve series circuits. Develop an equivalent model for a simple dc circuit; They share a single connection point. In the circuit shown at the right, a voltage of 6 v pushes charge through a single resistor of 2 ω. • the current in every part of the circuit (is the same, adds up). It = i1 = i2 = i3… given 120 v as the total voltage, and . Dc circuits are simply those in which the current moves in one direction. The total current in a series circuit is the same as the current through any resistance of the circuit. Calculate the equivalent resistance for series and parallel connected resistors.
Remember that in a series circuit: After that, it's a simple matter to calculate the voltage drops in each . It = i1 = i2 = i3… given 120 v as the total voltage, and . On a series circuit they should equal the voltage increase of the power supply. You will need to build circuits using a battery, light bulbs, and .

It = i1 = i2 = i3… given 120 v as the total voltage, and .
Develop an equivalent model for a simple dc circuit; In the circuit shown at the right, a voltage of 6 v pushes charge through a single resistor of 2 ω. A tutorial on how to solve series circuits. Calculate the equivalent resistance for series and parallel connected resistors. You will need to build circuits using a battery, light bulbs, and . On a series circuit they should equal the voltage increase of the power supply. They share a single connection point. Dc circuits are simply those in which the current moves in one direction. Each resistor in a series circuit adds to the total resistance. The total current in a series circuit is the same as the current through any resistance of the circuit. Remember that in a series circuit: This equation can be used for any number of resistors in parallel. After that, it's a simple matter to calculate the voltage drops in each .
After that, it's a simple matter to calculate the voltage drops in each . In the circuit shown at the right, a voltage of 6 v pushes charge through a single resistor of 2 ω. • here we have three resistors of different resistances. Equivalent resistance and current in a parallel circuit. On a series circuit they should equal the voltage increase of the power supply.

After that, it's a simple matter to calculate the voltage drops in each .
It = i1 = i2 = i3… given 120 v as the total voltage, and . This equation can be used for any number of resistors in parallel. You will need to build circuits using a battery, light bulbs, and . After that, it's a simple matter to calculate the voltage drops in each . Calculate the equivalent resistance for series and parallel connected resistors. • the voltage supplied by the battery is the ______ . Develop an equivalent model for a simple dc circuit; The total current in a series circuit is the same as the current through any resistance of the circuit. On a series circuit they should equal the voltage increase of the power supply. • the current in every part of the circuit (is the same, adds up). Select intro and build the simple series circuit included in this lesson. Dc circuits are simply those in which the current moves in one direction. Each resistor in a series circuit adds to the total resistance.
Simple Series Circuit Worksheet / Electricity Circuits Worksheets Simple Circuit Elementary Worksheets Electrical Circuit Diagram :. This equation can be used for any number of resistors in parallel. It = i1 = i2 = i3… given 120 v as the total voltage, and . Each resistor in a series circuit adds to the total resistance. In the circuit shown at the right, a voltage of 6 v pushes charge through a single resistor of 2 ω. Series circuits are the simplest to work with.
• the current in every part of the circuit (is the same, adds up) simple circuit worksheet. It = i1 = i2 = i3… given 120 v as the total voltage, and .
Tidak ada komentar :
Posting Komentar
Leave A Comment...